Distribution Inside the Facility
To distribute, demultiplex, transport and switch RF-over-fiber signals within and between facilities, different approaches are viable, depending on the application and operator preferences. The classic version is a hard-wired distribution: the incoming RF signals are fed to the electrical-optical converters on a splitter. Integrated amplifiers are mostly used here, since splitting reduces signal power. For instance, the signal level drops by about 3 to 4 dB with a 1:2 splitter. A distribution of 1:128 corresponds to an attenuation of approximately 26 dB. This very significant loss due to splitting must be addressed in addition to any line losses.
DEV Systemtechnik is a key supplier of equipment for RF signal distribution, switching and amplification functions, offering unique solutions in a single chassis. These products are available in different sizes and with different degrees of integration. Combining both the signal conversion and signal distribution in the same device delivers significant space and power consumption savings compared to conventional solutions.
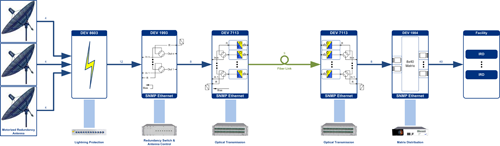
Figure 5 Overview of a complete signal path. (Source: DEV Systemtechnik)
Matrix Switching: Operating Efficiency, Control & Redundancy
Another, much more flexible option than “hard wiring” a facility is to use a Matrix Switch. This makes it possible to switch an input source to any number of outputs, or vice versa. With an RF Matrix Switch, it is no longer necessary to manually reconfigure the cabling or patch panels in order to change signal paths. Redundancies, optical-electrical conversion, and amplification can all be executed by a Matrix Switch. The device can be controlled remotely via a web browser or by an existing management system. The product portfolio of DEV Systemtechnik ranges from compact RF Matrix Switches with eight inputs and outputs to a 64 x 64 matrix, which can be assembled in a cluster, and delivers up to 2048 x 2048 inputs and outputs.
RF signal routing requirements within a facility differ, depending on the application. For programming acquisition, incoming satellite and/or fiber RF signals are transmitted to IRDs (Integrated Receiver Decoders) to decode the video, and/or feed it to the cable or IPTV system multiplex. If an IRD fails or suffers faults, the Matrix Switch can be used to feed a backup IRD or duplicate and route a problem signal to test equipment for testing and fault isolation.
On the outbound transmission side, matrix switches can also be used to route signals from IRD sources for forward distribution, for example to modulators for direct transmission onto an HFC (hybrid fiber/coax) cable network or to IPTV encoding and multiplexing systems for downstream distribution to set tops.
