
A circuit or system simulation is only as good as the component models used in the simulation. Simulating a design with insufficient models will produce simulation results that do not accurately predict the performance of the design when built and tested. Various real world factors associated with RF/microwave components can affect performance, including substrate-dependent parasitics and higher-order resonances. So, component models must capture these effects to assure design accuracy.
Modelithics® specializes in developing accurate measurement-based simulation models for RF/microwave components. The company’s premier product, the Modelithics COMPLETE Library™, consists of models for everything: passive components, transistors, diodes and more. Every model Modelithics provides is intended to be a value-add for designers, enabling accurate simulations leading to first-pass design success. Modelithics’ model libraries are available for six RF/microwave simulation software platforms, Keysight Technologies’ PathWave Advanced Design System, Keysight Technologies’ PathWave RF Synthesis (Genesys), Cadence AWR Design Environment, Ansys HFSS, Sonnet Suites and Cadence Virtuoso Spectre RF. The Modelithics COMPLETE Library contains over 750 models from nearly 70 suppliers, representing more than 18,000 components.
The Modelithics COMPLETE Library contains various sub-libraries: the CLR Library, which is a collection of capacitor, inductor and resistor models and the NLT and NLD libraries, comprising nonlinear transistor and nonlinear diode models, respectively. The Modelithics COMPLETE Library also includes the SLC, SPAR and Substrate libraries. The SLC Library contains linear and nonlinear models for system-level components like amplifiers and filters, while the SPAR Library is a collection of S-parameter, file-based models. The Substrate Library holds substrate property definition blocks for many popular substrates. The CLR, NLT, NLD and SLC libraries contain measurement-based equivalent-circuit models - not just simple S-parameter files - and the Modelithics COMPLETE Library includes various example projects, demonstrating how to use the models.
CLR LIBRARY FOR PASSIVE COMPONENTS
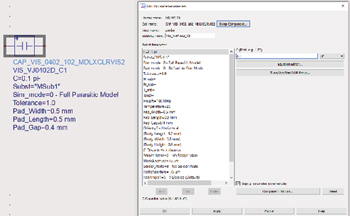
Figure 1 The Microwave Global Model for the Vishay VJ0402 capacitor family, which has a capacitance range from 0.1 to 82 pF.
The CLR library contains capacitor, inductor and resistor models from AVX, Coilcraft, Vishay and many other suppliers. This library features Modelithics’ Microwave Global Models™, advanced models developed by Modelithics that are part-value scalable. A single Microwave Global Model covers the full range of part values for a component series (see Figure 1). In addition to part-value scalability, Microwave Global Models scale with substrate and solder pad dimensions, to provide designers with flexibility, and the models accurately capture substrate-dependent parasitic behavior. Since a single Microwave Global Model covers the full range of part values for a component series, they are useful for tuning and optimizing a design.
NONLINEAR TRANSISTOR AND DIODE MODELS
The Modelithics COMPLETE Library contains the NLT Library, a collection of nonlinear transistor models for high-power and low-noise devices. This library comprises models for various HEMT, MOSFET and BJT transistors, as well as other technologies. The devices represent products from Qorvo, Mitsubishi, California Eastern Laboratories and others. Common device model features in the NLT Library include temperature and bias dependence. Model datasheets may include S-parameter data over temperature and varying bias conditions, and they typically have the DC current-voltage (IV) characteristics.
Using NLT Library device models, designers can simulate gain compression, power-added efficiency, noise (i.e., low-noise models) and other parameters, with the corresponding data found in the model datasheets. Certain model datasheets also have load-pull performance and some of the models are substrate scalable. The example projects with the Modelithics COMPLETE Library help users learn how to use NLT Library models to perform various simulations. For instance, example schematics are available that demonstrate simulations using different substrates and bias conditions and how to perform simulations analyzing load-pull and harmonic performance (see Figure 2).
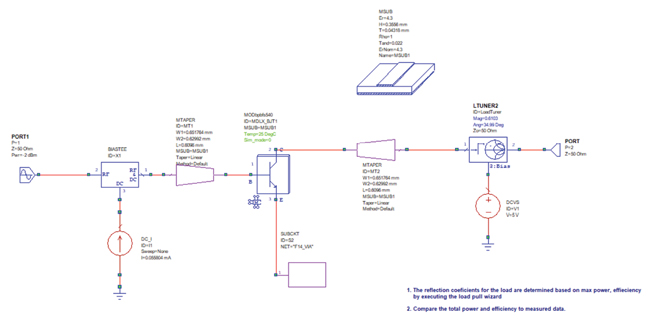
Figure 2 Example schematic for load-pull analysis.
The NLD Library comprises a collection of nonlinear diode models for various Schottky, varactor, PIN and step-recovery diodes from Infineon, MACOM, Skyworks and other suppliers. Substrate scalability, temperature dependence and bias dependence are three significant features of the NLD Library models. They are featured in example schematics that demonstrate simulations with varying substrates and bias conditions, with additional schematics illustrating simulations including S-parameters, power compression and harmonics.
SLC AND SPAR LIBRARIES
To complement the CLR, NLT and NLD libraries of active and passive equivalent-circuit models, the Modelithics COMPLETE Library includes the SLC and SPAR libraries. The SLC Library provides models for system-level components such as amplifiers, filters, attenuators, switches and transformers. The amplifier models in this library are nonlinear behavioral models that enable more than S-parameter simulation (see Figure 3): designers can analyze parameters such as 1 dB compression (P1dB) and the third-order intercept point (IP3). The models are validated over frequency and power ranges, which are listed in the datasheets. The SLC Library contains more than amplifiers, including filters, attenuators and switches. Again, substrate scalability is a significant attribute of these models. Among the suppliers represented in the SLC Library are Mini-Circuits, International Manufacturing Services and Barry Industries.
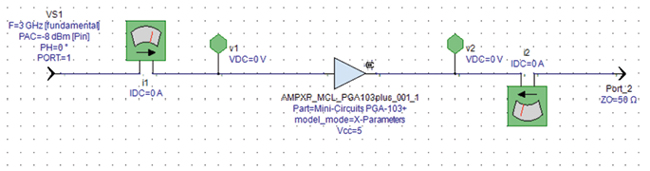
Figure 3 Example schematic for analysis of a Mini-Circuits amplifier using a nonlinear behavioral model.
The SPAR Library is a collection of S-parameter, file-based models for components like amplifiers and splitters. These models are more advanced than traditional S-parameter files; many of them contain multiple S-parameter data files activated with user-defined model settings. Multiple data files within a single model correspond to either different part values in a component series, different substrates or different bias conditions (i.e., for amplifiers), depending on the model. SPAR Library models are useful for tuning and optimization.
Modelithics Inc.
Tampa, Fla.
www.modelithics.com
sales@modelithics.com
