Radar systems are used to determine the presence, range, size, shape, and velocity of objects and can be classified as either imaging or non-imaging radar systems. Imaging radar systems create 2D images of target objects either through continuous wave signal or pulsed signal. The imaging radar system is prevalent in sectors such as industrial, agriculture, and healthcare, as well as environmental and weather monitoring applications. Non-imaging radar systems, also known as scatterometers, are used as speed gauges and radar altimeters.
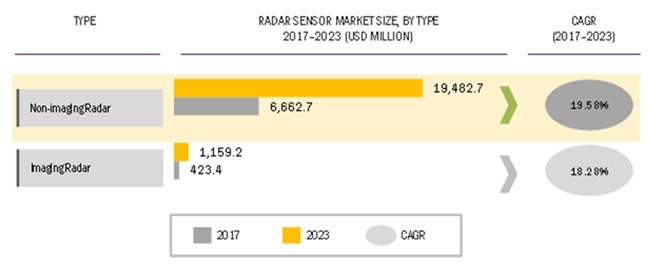
A radar sensor, along with the transmitter, receiver, duplexer, and antenna, are important components of a radar system. Radar sensors help in determining parameters such as velocity, range, shape, and size of the target object by transmitting either continuous wave signal or pulsed wave signal. According to MarketsandMarkets, the radar sensor market is projected to reach USD 20.64 billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 19.51% during 2017–2023.
Current outlook
Radar systems are used in a wide-range of end-user applications, including automotive, aerospace, and military, as well as security & surveillance, traffic monitoring and management, environmental and weather monitoring.
In automotive, a radar system is used as adaptive cruise control and autonomous driving assistance systems (ADAS). In ADAS, radar systems are used for applications such as lane change support, collision avoidance, and parking aid, as well as pedestrian and cyclist detection, and step-&-go functionality. A short-range sensor in automobiles helps in collision warning, lane change assistant, blind spot monitoring, and parking aid, whereas a long-range radar system helps in identifying blind spots in front of the vehicle and in determining traffic situation ahead of the vehicle. According to MarketsandMarkets, the contribution of automotive is the highest in the radar sensor market and will continue to be dominant in the coming years.
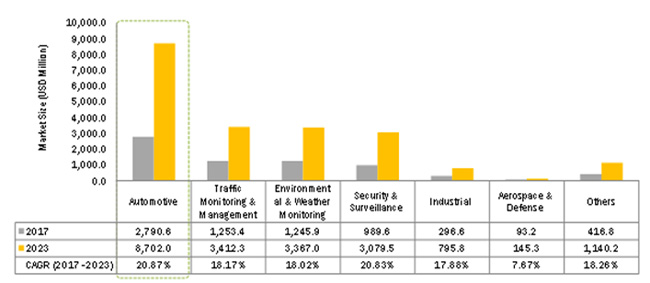
The military/defense is another major segment in the radar sensors market. In the military, radar systems are used in missile control, ground surveillance, navigation, and military air traffic control, as well as to identify moving targets and assist in search and rescue operations. Increased military spending will lead to the growing adoption of radar sensors. According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), global military spending increased by 2.6% in 2018 compared with 2017 in the US, China, India, France, and Saudi Arabia—top spenders that account for almost 60% of global military spending. Also, the increasing need for security and surveillance at borders has led to the requirement of advanced sensor network security system. This will propel the adoption of radar systems in the military/defense segment.
Future outlook
Growing developments in the space of self-driving/autonomous vehicles are likely to drive the adoption of radars. Automobile companies, such as Ford, GM, Tesla, and Volvo, are planning to release driverless cars by 2021. For instance, Ford is planning to deploy almost 1,000 driverless cars by 2021, Volvo is planning to offer 100 Swedish customers early access to their autonomous XC90 SUV by 2021, and Tesla is planning to release self-driving taxis (robotaxis) by 2020 in the US. Therefore, the introduction of driverless cars is likely to propel the adoption of radar systems during the forecast period.
Developments have been observed in integrated radar technologies. For instance, in May 2019, a team of researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology (Germany); the Fraunhofer Institute for Organic Electronics, Electron Beam, and Plasma Technology (Germany); and the Institute of High Frequency Technology at RWTH Aachen University (Germany) developed a process in which radar sensors can be coated on vehicle headlights. In May 2019, Libelium, a Spanish manufacturer of hardware and IoT solutions introduced a smart parking device for cars with integrated radar technology. Also, the continuous developments of military radar systems such as SPAR tiles from MACOM, Digital Array Row Transmitter (DART) from Lockheed Martin, and the Artisan 3-D radar system from BAE Systems help in the growth of the radar sensors market during the forecast period.
Competitive scenario
Robert Bosch Gmbh, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Infineon Technologies AG, Continental AG, and HELLA GmbH & Co. KGaA are among the leading vendors in the market. Robert Bosch has gained popularity in the radar sensors market due to continuous investments in products related to automotive. For instance, in January 2019, Bosch announced to invest USD 1.1 billion to increase chip production owing to the rise in the adoption of sensors in cars. Apart from Robert Bosch, other vendors, such as Continental, HELLA, and Infineon Technologies, dominate the market due to their strong foothold in automotive. Lockheed Martin’s dominance is attributed to its strong foothold in aerospace and defense. Autoliv Inc., BAE Systems plc, NXP Semiconductors N.V., Saab AB, and ZF Friedrichshafen AG are among the other major vendors in the radar sensors market.

