Figure 2 Multi-channel radar sensor developed by Analog Devices.
24 GHz Multi-Channel Radar
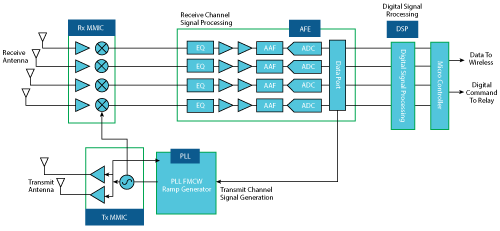
A 24 GHz radar is widely used in commercial and industrial applications, offering high accuracy, low power consumption and small size. These characteristics also make a 24 GHz radar a good fit for commercial and consumer UAV manufacturers, particularly considering the desire to reduce payload and power requirements. One such system developed by Analog Devices is shown in Figure 2.
A common misconception is the radar can operate at 77 GHz rather than 24 GHz. Current regulations dedicate the 77 GHz band to automotive vehicles and do not allow use with UAVs. While 77 GHz offers higher bandwidth for improved resolution, today’s regulations prohibit a 77 GHz radar being used for UAV applications.
When building a radar sensor, every dB improvement in receiver sensitivity extends the detection range. Most sensors available today focus on cost reduction, trading off phase noise and the number of channels. This trade-off degrades the receiver signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio, which limits the detection of smaller targets in the presence of larger objects. In real-world radar applications, busy or cluttered target scenarios cumulatively increase system phase noise and desensitize the radar receiver. The higher system noise masks or hides small targets and prevents object detection—detecting a narrow tree branch masked by the façade of a building—which can compromise UAV safety. Most single-channel, single chip, low-cost sensors do not provide the needed performance to make this distinction.
Using a 24 GHz multi-channel platform with higher performance, UAV manufacturers can:
- Use the FMCW radar mode to detect the range and velocity of objects up to 200 m with a resolution of approximately 60 cm; the resolution can be improved to 15 cm using an antenna design developed for the specific application.
- Achieve a field of view of approximately 120 degrees in azimuth and 15 degrees in elevation, depending on the antenna array design; using DBF, the field of view can be extended.
- Reduce power consumption while improving sensitivity 2x and extending the detection range 1.5x compared to traditional low-cost, single-channel radar sensors.
SUMMARY
The UAV/UAS market is growing quickly and offers tremendous potential for many new commercial applications. The landscape of sensor technologies is also changing rapidly, with newer sensor technologies such as light detection and ranging (LiDAR), time of flight (ToF) and ultrasonic being developed and adopted. UAV manufacturers should be aware of these newer options and incorporate the latest technologies as they mature.
However, radar remains the most compelling sensor technology, offering performance and versatility. To help the widespread commercial adoption of UAVs, UAV manufacturers need to lead the industry by embracing RF, microwave and mmWave radar, considering more than just the cost of the hardware, to demonstrate that UAVs can be safely operated autonomously.
Reference
