Terminology cont.
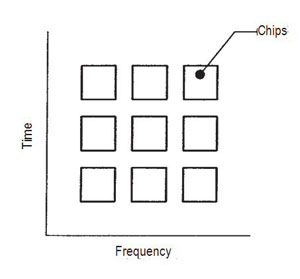
Figure 7 CDMA.
CDMA is used for spread spectrum secure communications systems. Figure 7 shows that CDMA assigns both time and frequency according to a code. These time/frequency allocations are called chips. Usually, a pseudorandom code is established at the transmitter and is received only by those receivers that have the same code; only they can receive the signal and demodulate it. This is the operating principle behind 3G cellular telephone network, ensuring the security of conversations.
Finally, a form of FDMA, called orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) has been adopted in recent years for use in 4G of cellular communications. It splits a serial data stream into several parallel streams transmitted through separate closely-spaced narrowband channels. These frequency channels can be closely packed in an efficient manner because their spectrums are orthogonal, or independent of each other. This has the effect of reducing interference and crosstalk without sacrificing throughput. This form of modulation and signal processing has found favor over CDMA in modern networks because of its resilience to fading and interference, and its spectral efficiency.
Radar. The earliest systems for Radio Detection and Ranging were developed just before and during WWII for the detection, characterization and tracking of airborne threats. Current applications are more diverse to include air and terrestrial traffic control, navigation, radar astronomy, ground mapping, weather prediction and more. Radar employs complex modulations superimposed on transmitted electromagnetic waves at microwave frequencies and higher. These are aimed and focused through sophisticated antenna systems in order to detect, characterize and track targets and subjects of interest with high accuracy and precision by reflecting the transmitted energy back to sensitive receivers with sophisticated signal processors.
Summary
This brief introduction and definition of some fundamental terms should provide a basis for subsequent discussions that address topics such as transmission media, components, solid state device, materials and measurements.
