This Strategy Analytics article reviews defense industry news over the course of 2015, covering radar, electronic warfare, weapons systems and communications summarizing our coverage through the Strategy Analytics’ Industry Reviews. The report also looks at microwave, optoelectronic and other components as well as discussing business event, product announcements, milestones and contract activity.
January
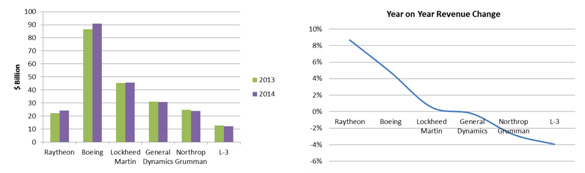
January saw companies reporting financial results with a snapshot of year on year results for 2013-2014 showing a mixed bag. Raytheon and Boeing were the star performers with year-on-year growth of 10% and 5% respectively while Lockheed Martin and General Dynamics were flat. Results for Northrop Grumman and L-3 left room for improvement, failing to show year-on-year growth. Northrop Grumman was able to improve year-on-year profitability while L-3’s profitability declined 12% year-on-year.
Snapshot of Year-on-Year Financial Performance
Other notable developments during January included:
· Beriev Aircraft reportedly preparing an AEW variant of the Ilyushin upgraded transport aircraft, Il-76MD-90A, fitted with a panoramic radar system with a rotating antenna capable of active electronic vertical scanning and mechanical bearing scanning.
· The Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) advanced EW suite, which features a radar warner and jammer, completed its first flight onboard the Tejas-PV1 light combat aircraft (LCA) in Bengaluru.
· The UK MoD awarded MBDA Missile Systems UK a contract to keep developing the land-based future local area air defense system (FLAADS) to replace the aging Rapier system.
· Raytheon and L-3 were both working to accelerate the Military GPS User Equipment (MGUE) program through the addition of pre-prototype receiver card deliveries and test support activities to enable faster fielding of M-Code capable GPS receivers.
· COM DEV International completed the purchase of 100 percent of MESL Microwave Ltd, while L-3 Communications acquired the assets of MITEQ. These will be combined with L-3's Narda Microwave-East with the new entity to be called L-3 Narda-MITEQ.
· The F/A-18 Super Hornet infrared search and track (IRST) system, developed and integrated by Boeing and Lockheed Martin, received approval from the U.S. Navy to enter low-rate initial production.
February
Radar developments in February underscored the growing maturity and use of both AESA-based radar systems, and GaN technology. Northrop Grumman is under contract to Lockheed Martin to supply 142 AN/APG-83 Scalable Agile Beam Radar (SABR) systems as part of the Taiwan Air Force F-16 upgrade program. Saab meanwhile has been chosen by Northrop Grumman to provide components and subsystems of the US Marine Corps AN/TPS-80 Ground/Air Task Oriented Radar (G/ATOR) system. AESA technology also underpins Lockheed Martin UK Integrated Systems (UKIS) bid for the UK Royal Navy's (RN's) Crowsnest airborne surveillance and control (ASaC) program. Raytheon, meanwhile, received approval from the US Government to export a GaN AESA Patriot sensor to Patriot Air and Missile Defense System partner nations.
GaN will also underpin future EW systems such as the US Navy's Surface Electronic Warfare Improvement Program (SEWIP) contract. Northrop Grumman won a contract for the next phase of the $5.3 billion program, beating out a Lockheed Martin-Raytheon partnership.
Smart weapons/missile activity included a range of contracts with Raytheon notably supporting a broad range of systems. In related news, Finmeccanica-Selex ES signed a contract with MBDA France and Sagem to support the development and production of an infrared seeker for the anti-surface guided weapon (heavy) / anti-navire léger (FASGW(H)/ANL) missile.
Merger and acquisition activity in the defense industry had seen some prominent deals since the beginning of the year with ATK and Orbital combining to become Orbital ATK, Inc. In February, Harris and Exelis announced a definitive agreement with Harris acquiring Exelis for $4.75 billion to focus on the defense (as well as aerospace and aviation) sectors. Finmeccanica was also taking steps to align its operations more tightly with the defense sector by transferring its loss-making rail business to Hitachi Ltd.
Contract activity included Israel’s continuing commitment to the Lockheed Martin F-35 with a $2.82 billion deal for 14 aircraft as well as other technological and training elements, and an option to buy another 17 units. Dassualt is finally getting some traction with the Rafale, and will supply 24 Rafale fast jets as part of a $5.7 billion French government package deal with Egypt that also includes a French frigate and an MBDA air defense missile system.
Finally, UAS activity included a US Navy LRIP contract for Northrop Grumman’s MQ-4C Triton UAS (formerly known as Broad Area Maritime Surveillance (BAMS) UAS). General Atomics ASI’s MQ-9 Reaper UAS is under consideration by the Netherlands and other European activity included the maiden flight of the Piaggio Aerospace P.1HH HammerHead.
March
Establishing EW capabilities from space underpinned a contract awarded to Airbus Defence and Space (Astrium) to enable the design and construction of a military spaced-based SIGINT system named Capacite de Renseignement Electromagnetique d'origine Spatiale (CERES) for France. CERES will provide the French armed forces with an operational space-based SIGINT capability from 2020, with three closely positioned satellites providing detection and location of radiocommunications and radars.
Airborne EW activity included contracts for Raytheon to provide Miniature Air Launched Decoy Jammer (MALD-J) missiles, while Mercury Systems received follow-on orders to deliver DRFM jammers. Shipborne EW activity meanwhile was underscored by Northrop Grumman’s contract to develop and manufacture the next-generation surface EW improvement program (SEWIP) Block 3 system, which will be underpinned by AESA technology to enable active arrays, which in combination with passive arrays will perform electronic warfare and communications functions.
The proliferation of AESA-based radar systems continued to be evident in radar-related news. India is reportedly planning to commission a series of airborne early warning aircraft that will feature indigenously developed AESA radars. Meanwhile, the USAF was considering its AESA radar options for the National Guard F-16s against a backdrop of limited funds. On the contract front, there was ongoing activity for both Raytheon and Northrop Grumman, while Lockheed Martin chose Rada’s AESA Multi-Mission Hemispheric Radar (MHR) to be an integral sensor for the company’s high energy laser weapon system.
Weapons systems activity included a number of European teaming agreements including Thales signing a new cooperation agreement with Aselsan to continue the joint development of a missile launcher system; Diehl Defence signing an exclusive teaming agreement with Orbital ATK on marketing and manufacturing the Advanced Anti-Radar Guided Missile (AARGM) in Germany; and Raytheon signing a Letter of Intent with MESKO, Poland's missile and ammunition manufacturer, for a range of activities including collaboration on a next generation anti-armor weapon and a very short range air defense weapon.
Defending communication systems underpinned a contract to Rockwell Collins to provide its MicroGRAM GPS receivers for Harris' tactical radios, bringing secure, jam-resistant GPS capability to products such as the Falcon III AN/PRC-158 and AN/PRC-117G. DRS received a contract for tactical integrated communications systems for the Royal New Zealand Navy's ANZAC-class frigates while General Dynamics is to provide product support services for the sustainment of AN/PRC-154and AN/PRC-154A radios.
April
Demand for European radar technology based around solid-state and AESA architectures led to contracts for Kelvin Hughes, Saab, Selex ES and Thales in April:
· Kelvin Hughes was contracted to supply its SharpEye radars for the UK Royal Navy's new River class Batch 2 Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPV).
· Saab will be upgrading the sensor on Norway’s Arthur (ARTillery HUnting Radar) weapon-location radar system to Saab's current production version of Arthur (ModC).
· Selex ES will be supplying its Seaspray 5000E AESA surveillance radars for Australia’s search and rescue platforms.
· The Netherlands MoD chose Thales for the supply of air defense systems and services to the Netherlands MoD, which will include the supply of SMART-L early warning capability (EWC) ground-based systems.
An emphasis on EW system development was underpinned by operational tests of Raytheon’s Miniature Air Launched Decoy-Jammer (MALD-J), and Exelis and L-3 partnering to provide electronic self-protection capabilities for an airborne platform.
There was an array of announcements in the weapons and communications sectors also, with both contracts and system developments. Optoelectronic and other sensor technology announcements included contracts for Northrop Grumman and Selex ES to provide LAIRCM and IRST systems respectively.
April also marked company result announcements with a mix of results. Most companies were able to show some growth in some, if not all of their different business groups, but the general trend showed revenues declining while profitability was being maintained through operational optimisation. Cyber, RF and optoelectronics underpinned acquisition activity by the likes of Raytheon, API Technologies and Teledyne.
May
The defense industry’s endeavors to strike a balance between scale and capability were exemplified by significant acquisition and investment activity in the month of May. Harris completed its previously announced $4.75 billion acquisition of Exelis; the combined company is expected to generate combined revenues of over $8.21 billion leveraging the respective strengths of the two companies across areas including tactical communications, electronic warfare and night vision. Elbit Systems and Raytheon acquired capabilities in the area of cyber/intelligence with their respective transactions.
At the other end of the supply chain scale, suppliers of semiconductor components used IMS 2015 to introduce new products to the market place that they hope will underpin the next generation of radar, communications, electronic warfare and other systems. GaN semiconductor technology underpinned many of these announcements, with high power capability being married with other attributes such as linear performance and millimeter wave operation as showcased by a Ka-band GaN MMIC from Northrop Grumman. MACOM meanwhile introduced the next generation of its GaN-on-Si technology claiming performance parity with GaN-on-SiC, while Qorvo and Freescale offered plastic packaging in conjunction with the high power attributes typically associated with GaN-on-SiC devices.
At the module level, GaN underpinned offerings from API and Diamond Technologies and this extended through to the system level with Airbus Defense and Space contracted to provide an additional GaN-based TRS-4D AESA naval radar for the U.S. Navy’s Littoral Combat Ship (LCS) program. Raytheon completed the AN/SPY-6(V) Air and Missile Defense Radar (AMDR) critical design review confirming amongst other things the maturity, producibility and low risk of the GaN-based Radar Modular Assemblies that will underpin this next generation radar system.
The flip side of the unprecedented capabilities that will be offered by next generation radar systems is the challenge it represents to the Electronic Warfare community. To this end, Exelis and Leidos have been selected to continue to evolve advanced technology development for the DARPA Adaptive Radar Countermeasures (ARC) program which is designed to developed EW systems that will be capable of electronically defending assets against these emerging radar threats.
Finally, directed energy systems took one step closer to being fielded in the case of the HELLADS program. DARPA's High-Energy Liquid Laser Area Defense System (HELLADS) demonstrated sufficient laser power and beam quality to advance field tests at White Sands Missile Range over the coming months against rockets, mortars, vehicles and surrogate surface-to-air missiles.
June
The second quarter of 2015 ended with more divestments, mergers and acquisition news. Kratos Defense & Security Solutions acquired Herley Industries in 2011 for $270 million to augment the company’s C4ISR offerings with RF, microwave and millimeter-wave components and subsystem capabilities to support defense and aerospace systems including radar, electronic warfare and communications and other. While the theory behind expanding capabilities was sound, Kratos’ continuing losses catalysed a decision by Kratos management to sell these operations to Ultra Electronics for $265 million allowing Ultra to expand its capabilities, with some reports suggesting a focus on tapping into the US electronic warfare sector.
Other transactions included Samsung completing the divestiture of its defense business, Samsung Techwin Co., along with joint venture Samsung Thales Co. to Hanwha Group for $2.35 billion, and United Technologies confirming that it is pursuing options to divest or spin-off the Sikorsky division.
Contract activity across radar, weapons systems, EW and communications/navigation was robust in terms of contracts and other developments.
· Thales’ Ku-band I-MASTER radar was selected by the Royal Jordanian Air Force and was also demonstrated on Textron AirLand's Scorpion Jet. The company also introduced the STAR NG S-band PSR system suitable for both civil and military ATC.
· Selex ES received a contract from Embraer Defense and Security to provide an undisclosed number of X-band Gabbiano T20 radar systems for the Brazilian Air Force’s KC-390 transport aircraft. The company was also selected to provide a SAGE 600 digital Electronic Support Measure (ESM) system for the Indonesian Air Force.
· Electronic warfare developments also included contracts for Boeing and Raytheon related to the NGJ program, with the former chosen to integrate the NGJ pod onto the EA-18G aircraft.
· Weapons systems news included Raytheon and Kongsberg signing an agreement to extend their partnership on the National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System (NASAMS). Raytheon’s Patriot system was overlooked by Germany however which appears to be leaning towards the MEADS systems developed under a joint project between Lockheed Martin, MBDA Italia and MBDA Deutschland.
· Communications activity included Airbus Space and Defense being contracted to provide Skynet services to the Norwegian MoD. Skynet 5 is the UK MoD’s hardened X-band satellite constellation plus associated ground network that provides all BLOS communications to the UK MoD. Northrop Grumman meanwhile was contracted to provide BACN JUON payload operations and support, and was also highlighting milestones in the CANE program.
At the technology level, Raytheon was highlighting the company’s GaN technology as it works towards upgrading the Patriot system with an AESA architecture populated with GaN-based transmit-receive units.
July
The third quarter of 2015 continued with a number of announcements related to acquisitions and mergers, as well as joint ventures:
· Harris Corporation announced its new organizational structure following its acquisition of Exelis as well as confirming business unit and headquarter locations.
· Airbus Helicopters is teaming up with Mahindra Defence with the resulting joint venture to act as the prime contractor for India’s military helicopter tenders including the Reconnaissance and Surveillance Helicopter, the Naval Utility Helicopter and the Naval Multirole Helicopter procurement programs.
· Lockheed Martin entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Sikorsky Aircraft for $9.0 billion with plans to align Sikorsky under the Lockheed Martin Mission Systems and Training (MST) business segment, leveraging existing partnerships on a number of critical programs, including the VH-92 Presidential Helicopter, Combat Rescue Helicopter and the Naval MH-60 Helicopter.
· Kant will be name of the new merged entity comprising German tank manufacturer Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) and French armored vehicle maker, Nexter Systems.
Contract activity remained robust across platforms and systems with radar, communications and weapons systems dominating the latter category:
· RADA Electronic Industries Ltd. received contracts for its Multi-Mission Hemispheric S-Band AESA radar (MHR) system from both a European country and the US.
· Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman will be the primary contractors for the Republic of Korea’s KF-16 upgrade program which we assume will incorporate Northrop Grumman’s AESA Scalable Agile Beam Radar (SABR) system.
Profitability was being maintained in the reported company financials, which continue to reflect an industry that is struggling to find revenue growth. While there are individual segments that are showing growth, overall numbers remaining largely flat.
· Lockheed Martin reported second quarter 2015 net sales of $11.6 billion, compared to $11.3 billion in the second quarter of 2014.
· Northrop Grumman reported second quarter 2015 revenue of $5.9 billion compared to $6.0 billion for the prior year quarter.
· Raytheon announced net sales for the second quarter 2015 of $5.8 billion compared to $5.7 billion in the second quarter 2014.
August
Unmanned systems news encompassed ground, sea and airborne platforms in August, with contract activity as well as ongoing development work on both existing platforms and new concepts.
· iRobot Corp will supply Small Unmanned Ground Vehicles (SUGV) to the U.S. Marine Corps Systems Command, while Spain will reportedly acquire four Reaper surveillance drones and two ground stations from General Atomics.
· Northrop Grumman completed a series of high-altitude, long-endurance RQ-4 Global Hawk demonstrations, designed to showcase the abilities of the platform’s mission management and control systems to respond to external requests to alter flight routes and sensor functionality. Separately, the company also successfully demonstrated the endurance capabilities of the MQ-8C Fire Scout.
· The European UCAV, nEUROn, completed a series of operational tests, flying 12 sorties to verify its combat capability, low-radar-cross section and low-infrared signature.
Developments at the semiconductor level focused on power electronics, as well as a focus on new technologies.
· PowerAmerica and Lockheed Martin are partnering on projects to accelerate the commercialization of wide bandgap power electronics technologies.
· DARPA’s three-phase Circuit Realization At Faster Timescales (CRAFT) program aims at develop new fast-track circuit-design methods, establishing multiple sources for integrated circuit fabrication, and maintaining a technology repository.
· BAE Systems announced that the company’s next-generation 45 nm ASICs microchips achieved Qualified Manufacturers Listing (QML) certification and are now ready to be deployed on satellites.
Business related activity included news related to a number of acquisitions covering RF component and subsystem companies.
· HEICO Corp acquired 80.1% of the shares of privately held Midwest Microwave Solutions, whose front-end RF and Microwave hardware is used by the U.S. Intelligence Community for Signal Intercept applications.
· Ultra Electronics completed its acquisition of the Electronic Products Division (EPD) of Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, a designer and producer of RF and microwave integrated systems and subsystems for use in EW, radar, communication, missile, flight test and simulation applications.
September
September saw a number of developments at the component level coinciding with the European Microwave Week series of conferences. Strategy Analytics attended and spoke at the annual Defense, Space and Security Forum discussing the expanding role of UAS platforms and the opportunities this presents for payload and enabling technology suppliers. DSEI (Defence Security and Equipment International) was also held in September and provided a showcase for suppliers of defence and security equipment.
Gallium nitride (GaN) was the primary focus for company announcements with companies showcasing both capabilities across a range of powers and frequencies to target various applications:
· Pasternack expanded their offering of GaN coaxial power amplifiers offering products that feature gain levels from 43 to 60dB across a broad range of frequency bands ranging from 30 MHz to 7.5 GHz. The connectorised power amplifiers feature saturated output power levels ranging from 10W to 100W with 20 to 35% PAE.
· Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd introduced an X-band GaN IMFET device targeting radar applications that provides over 200 W output power in pulsed operation.
· Diamond Microwave announced a ten-fold increase in its power output capability with the addition of a 1 kW X-band model to the company's range of GaN-based pulsed SSPAs. The DM-X1K0-01 is targeted as a replacement for TWTAs.
· Wolfspeed is the new name for the Power and RF division of Cree and the subsidiary was released reportedly the highest power C- and S-band GaN HEMTs to target radar systems employing traditional TWT amplifiers.
· Qorvo announced three new GaN RF transistors in low-cost plastic packages designed to enable smaller size and greater reliability in civilian marine, airborne and infrastructure radar systems operating in the 8-12 GHz frequency.
RF MEMs technology has been explored for many years with varying levels of success. Tronics and Airbus Group announced their partnership for the development of capacitive MEMS-based RF switches and circuits. Initial collaboration has demonstrated the feasibility and functionality of integrated devices that incorporate hermetic wafer level packaging (WLP), and now enters its second phase in order to further improve the performance and maturity of the technology.
At the sub-system level, API Technologies announced the expansion of its field-upgradeable line of AESA radar system and subsystem solution elements with the addition of a 2D Steerable Active Antenna Array featuring fully interchangeable and factory calibrated Quad Transmit Receive Modules (QTRMs).
There is also a growing recognition to develop systems that can counter UAS platforms with Blighter Surveillance Systems, Chess Dynamics and Enterprise Control Systems adding new capabilities to their anti-UASA defense system (AUDS), including a quad band RF inhibitor / jammer, an optical disruptor and rapid deployment.
October
The high profile Long Range Strike Bomber LRS-B program competition reached an intermediate conclusion with the US Air Force awarding Northrop Grumman a potential $55.0 billion contract. The program has completed preliminary design review and manufacturing readiness review, and the platform designs are at the subsystem level. The Air Force expects to purchase up to 100 LRS-B aircraft. Northrop Grumman beat out a Lockheed Martin/Boeing team to win the competition with the losing team working towards lodging a protest to ensure that another large US program will be off to the usual lethargic start which will no doubt translate to delays and cost overruns. Notably, Raytheon was not part of any bidding team but is one of the guaranteed winners as the company will no doubt be in a primary position to supply key systems such as radar and EW, which will no doubt take advantage of AESA architectures, GaN RF front-ends and digitization of the RF signal ever closer to the antenna.
Nearer term activity on radar and EW systems emphasized the ongoing importance that GaN technology will play in next generation systems.
· The US MDA contracted a Lockheed Martin-led team to develop, build and test the GaN-based Long Range Discrimination Radar (LRDR) to support a layered ballistic missile defense strategy.
· Lockheed Martin’s confirmed the long-term reliability of Wolfspeed’s GaN HPAs that will underpin Space Fence.
· Northrop Grumman received an engineering, manufacturing and development (EMD) contract to further mature system designs for the AN/SLQ-32(V)7 (SEWIP B3) electronic warfare system which will also use GaN.
· Advantech Wireless completed delivery of its Engage class 1.2m Flyaway VSAT terminals; the RF section incorporates interchangeable GaN-based 50W X-Band, a 50W Ku-Band or a 20W Ka-Band block upconverters.
The emphasis on next generation radar, EW and other sensor technologies is also continuing drive opportunities in the retrofit market.
· Raytheon is constructing a GaN-based AESA full size main panel radar array and says it is on track to having a full-scale main array demonstrator operational in early 2016 that will underpin an upgrade to the Patriot Air and Missile Defense System radar capabilities.
· Lockheed Martin completed the maiden flight of the F-16V, marking the first time the F-16V configuration has flown with Northrop Grumman's APG-83 AESA Scalable Agile Beam Radar (SABR). The F-16V "Viper" will include a range of other enhancements to collectively add significant combat capabilities.
· Boeing is working with BAE Systems on the U.S. Air Force’s Eagle Passive Active Warning Survivability System (EPAWSS) which will be used to upgrade more than 400 F-15Es and F-15Cs, replacing the Tactical Electronic Warfare System also known as TEWS, and keep the platform combat-worthy into the 2040s.
November
The UK MoD announced its Strategic Defence and Security Review (SDSR) in November including a focus on the RAF and most prominently a long overdue replacement for its maritime patrol aircraft, the Nimrod. It plans to expedite into service the Boeing P-8 Poseidon with a total order of nine examples. The £178 billion ($270 billion) SDSR plan also boosts the RAF capability in several other surveillance areas such as the Sentry and Rivet Joint as well as enhancing Typhoon squadrons which will have better ground attack capability and AESA radar. The announcement also reaffirmed commitment for the acquisition of Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning IIs.
In radar, the month included two examples of system upgrades via gallium nitride (GaN) based front-end circuitry from Raytheon and Lockheed Martin. An FMS deal could mean Poland becoming the first to receive the upgraded AESA radar system equipped Raytheon Patriot missile-defense system; Phase 3 should see the AESA version with full 360° coverage without rotation become operational. Meanwhile, Lockheed Martin announced its next generation radar technology: the Digital Array Row Transceiver (DART) based on GaN integrated circuits for systems upgrade or new builds. The technology is available in the recently launched TPS-77 Multi Role Radar system and is fully compatible with legacy products (TPS-77, TPS-59, FPS-117).
The month in EW began with the announcement of Raytheon, in partnership with the U.S. Navy, completing the Preliminary Design Review (PDR) for the Next Generation Jammer (NGJ) program. The Navy plans to declare Initial Operating Capability for the Jammer in 2021; NGJ is replacing legacy ALQ-99 jamming pods for the EA-18G Growler. At the Dubai Air Show, Elettronica announced it is to work on an escort jammer pod, called ELT/568, using active phased array antennas for jamming of a range of radar threats operating in lower bands. Contracts were sparse in November but BAE, Nashua, and Northrop Grumman Systems were each awarded contracts for AC/MC-130J radio frequency countermeasures.
In comms and nav, contract awards included Raytheon upgrading encryption modules in a satcoms system for the B-2 bomber while Rockwell Collins is to support the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command (SPAWAR) with standard airborne radios. Also, the US Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command awarded a contract to Data Link Solutions (DLS), the joint-venture between BAE Systems and Rockwell Collins, to provide multifunctional information distribution system (MIDS)-on-ship (MOS) systems. U.S. Special Operations Command awarded Harris a $390 million contract for Special Operations Forces Tactical Communications handheld radios. Finally, Northrop Grumman demonstrated its Freedom 550 gateway radio terminal that performs as a communications relay among fourth and fifth-generation aircraft.
Contract awards in weapons were helped by Middle Eastern countries, and likely others in due course, ordering replenishment stocks following expenditure in local conflicts. The US State Department responded to the Government of Saudi Arabia's request for air-to-ground smart munitions and associated equipment likely to be worth $1.29 billion. Among the request were Paveway II LGBs, BLU-117/MK-84 2000lb GP bombs. Similarly, there was a possible FMS to the United Arab Emirates for Joint Direct Attack Munitions and support worth $380 million.
Finally, on the business front, Lockheed Martin completed its acquisition of Sikorsky and Honeywell expanded its satellite business by acquiring COMDEV and Satcom1.
December
Platform and system upgrades as well as continued momentum behind next generation platforms closed out 2015 as well as setting up 2016 and beyond.
On the communications front, the French MoD is starting to look beyond its Syracuse military communications with the French DGA awarding a Thales Alenia Space-Airbus Defence and Space consortium for the construction and launch of two military communications Comsat NG satellites for the French armed forces. The UK MoD awarded Roke Manor Research a contract to develop an innovative data link solution underpinned by 3G COTS technology capable of transmitting real-time images and video from high altitude pseudo satellite UAS platforms such as the Airbus Defence & Space Zephyr.
Radar systems news including the European Space Agency working with Thales Alenia Space supplying the T/R modules and the front-end electronics and Airbus Defence and Space Satellites to build two additional Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Antenna Subsystem (SAS) for the Sentinel-1C and Sentinel-1D on the Copernicus program. Airbus Defence and Space completed Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT) of the first TRS-4D C-band GaN-based AESA multifunction air/surface radar destined for the US Navy Freedom variant Littoral Combat Ship (LCS).
Lockheed Martin is leading F-16 upgrade efforts for a number of countries and December saw the company receive contracts to support both Singapore and Taiwan with their respective upgrade programs. The company was also in receipt of a contract for long-lead materials, components and parts as well as logistics support for the fifth generation F-35 platform.
The Russian fifth generation platform is reportedly moving closer to being operational with trials ongoing to prove the flight performance of the T-50 PAKFA as well as testing of the multifunction integrated AESA radar.
The year also closed out with a number of business deals with the German Government approving the merger of tank manufacturer Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) with French armored vehicle maker Nexter Systems. Saab has formed a joint venture with UMS Aero Group that will take responsibility of marketing the former's Skeldar V-200 unmanned helicopter; the JV will also market UMS UAS. Communications was another focal point for business deals with Cubic Corp acquiring GATR Technologies and TeraLogics in a push to grow its defense systems business and expand its C4ISR offerings, and Comtech Telecommunications moving closer to acquiring TeleCommunication Systems.
Summary
2015 started with the defense industry showing mixed results as far as financials were concerned. This set the stage for defense industry players to look at growth through scale and the year closed out with a number of business deals including acquisitions and joint ventures. Atechnology-driven emphasis underpinned activity as the year progressed, driving platform and system upgrades as well as continued momentum behind next generation platforms.
