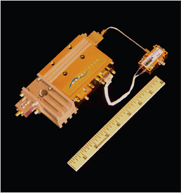
Demand for higher data rates and greater mobility in satellite communications is driving the need for smaller, lighter, more efficient and less costly power amplifiers. Using its patented spatial power combining, Wavestream has introduced a 25 W P1dB Ku-band power amplifier that draws under 200 W DC and fits in a rugged, compact 2.5 lb package.
Intended to provide a solution for integrators developing satellite communications-on-the-move (COTM) and micro-flyaway terminals at the commercially available Ku-band frequencies, this product provides the high power desired in a small and efficient package that enables the terminal manufacturers to tightly integrate it into their systems. The specific power amplifier requirements for these terminals include:
• high output power – to meet new data rate requirements
• small footprint – to fit inside micro-flyaway single-box systems or on COTM antennas
• low profile – to maintain the low profile of a micro-flyaway box and allow placement near feed for COTM
• low power dissipation – to minimize thermal management issues and weight of heat sinks in these very compact systems
• lightweight – to enable placement on in-motion axes of COTM antennas and minimize weight of micro-flyaway systems
• low cost – to enable widespread adoption of these new and more mobile communication solutions
The 25 W PowerStream™ Deck Power Amplifier (DPA) provides impressive performance against all of these requirements with its spatial power advantage.
Spatial Power Advantage
Solid-state power amplification has spread dramatically from cell phones to satellite terminals because of its high reliability, compact size and low cost. The use of SSPAs for satellite communications has been limited by the amount of power generated by individual transistors and the ability to efficiently combine the outputs of many transistors.
Binary microstrip combining efficiently combines only about 16 transistor outputs on a single chip. Binary combining efficiency deteriorates as the number of combined transistors increases, due to ohmic loss in each combining stage. Commercially available Ku-band MMICs currently reach maximum power of around 8 W.
Demand for higher power than individual MMICs provide has resulted in SSPA architectures that combine many MMIC outputs using microstrip and/or waveguide combining. These combining networks are lossy and bulky, and the resulting SSPAs are costly to manufacture, and too large and heavy for many portable applications.
Rather than combining in multiple steps, with increasing loss and size for each combining stage, the spatially power combined amplifier combines all transistor outputs in a single step. Many amplifying elements synchronously amplify the input signal, and their outputs are combined in free space for very high combining efficiency. The PowerStream Deck Amplifier stacks up cards containing traditional MMIC amplifier chips for spatial combining of their outputs to achieve high power density and high efficiency.
PowerStream Deck Amplifiers
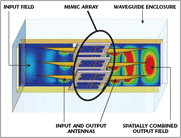
The PowerStream Deck Amplifier module contains an array of solid-state MMIC amplifier chips mounted on cards stacked in a waveguide enclosure (see Figure 1). Imprinted on each card are input antennas that receive a portion of the input signal and output antennas that radiate a portion of the amplified output. These outputs coherently combine within the waveguide, creating the high power output of the module.
The Deck Amplifier architecture provides significant advantages over traditional SSPAs in two ways:
• single-stage combining in air makes them highly efficient. The Deck Amplifier has demonstrated very close to 100 percent combining efficiency, independent of the number of devices combined.
• flexibility of the stacked card architecture reduces amplifier cost and improves efficiency. The number of cards and chips per card can be varied for optimum operating power with the fewest MMICs. Available chip-level power directly determines the number of chips to reach the desired output level, whereas in binary power combining the number of chips must be a power of two.
Based on this Deck Amplifier module, Wavestream has developed several power amplifier products aimed at the satcom industry. In addition to the Deck Power Amplifier featured here, the company has introduced a 25 W Ku-band Block Upconverter that is so small and light that it can be mounted on the feed of 1 m or larger antennas.
Deck Power Amplifier
When Wavestream introduced the first Deck Power Amplifier (DPA) product in 2005, it was considered to be the smallest, lightest and most efficient 25 W Ku-band power amplifier available. Several integrator’s in the target market of COTM and flyaway terminals quickly saw that this was a component that could provide them with a competitive advantage at their system level.
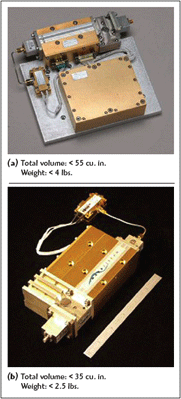
The DPA consists of a Deck Amplifier module, a driver amplifier, a power supply, and the isolator and launches necessary for the configuration. In the original product release, the power supply was a separate module located near the Deck Amplifier module, as shown in Figure 2. While this configuration was already compact, the company has now improved the product to incorporate the power supply inside the housing of the Deck Amplifier module, also shown, eliminating cabling and connectors and reducing the overall volume of the package significantly. Comparison photos also show the reduction in volume and weight for the two versions; the integration of the power supply into the Deck Amplifier module reduces both volume and weight by more than one third. For terminals already filled to capacity that are being looked at to provide additional features or functions, this space reduction is a real enabler.

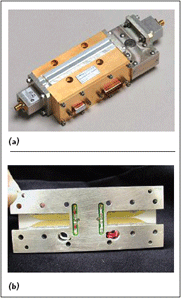
The Deck Amplifier module used in this product (see Figure 3) uses three cards stacked to produce the 25 W P1dB output. The cards, also shown, each contribute a third of the total output power. By using only two active cards, a highly efficient 16 W P1dB module can also be built in the same form factor. Additional products based on the 16 W version of the module are planned for release in 2006 as well. The maximum dimensions of the product are 7.5" L × 2.3" W × 1.5" H. This includes an output isolator and both input and output coaxial launches, which are required for some configurations. For configurations not requiring the output launch (WR-75 output), the total length is 6.55". Typical output power and DC draw curves for the three-card configuration are shown in Figure 4. In addition to the 14.0 to 14.5 GHz performance shown, this product is also specified to cover the extended Ku-band from 13.75 to 14.5 GHz, with less than 1 dB reduction in rated output power below 14 GHz.
The line driver module, shown in Figure 5, provides about 25 dB of additional gain necessary to take the typical output level of available L- to Ku-band upconverters up to the required input level for the Deck Amplifier module. This module was developed specifically for this product to be extremely compact, measuring just 2" L × 1.5" W × 0.75" H, including connectors. Later this year, this line driver will be available in a direct mount version, which attaches to the end of the Deck Amplifier module, replacing the current launch. This will reduce the overall size of the DPA slightly and simplify the already straightforward installation of the product even further.
The key development that enabled the reduction in size and weight of the DPA is the integration of the power converter into the Deck Amplifier module itself. The power supply provides conversion of +48 V or +28 V prime DC supply to the individual bias levels required for each of the cards in the module and also for the line driver module. In addition, the power supply provides a set of discrete monitor and control interfaces to ensure proper power-up sequencing and provide status. Protective functions such as transmit enable required and overtemp auto shut-down are incorporated. The newly designed power supply card, which fits into the well of the new Deck Amplifier module, is shown in Figure 6. This card provides all the required functionality in about 1.25" × 2.5" of floorplan space.

The Deck Power Amplifier’s compactness is greatly enhanced relative to alternative SSPAs by the reduction in thermal management needed to cool it. The DPA’s high efficiency enables the production of 25 W P1dB output power from a total DC power draw of under 200 W. Typical 14 to 14.5 GHz 25 W SSPA units consume over 300 W DC. This one-third reduction in power consumption reduces the heat sink and cooling system size and weight, and may enable a much smaller system package size.
Benefits of the DPA
The PowerStream DPA provides system-level benefits over other solid-state approaches by improving on performance for the key requirements for mobile and transportable satcom terminals:
• high output power – generates over 25 W of 1 dB compressed output power

• small footprint – 6.55" × 3.5" footprint for Deck Amplifier module plus 2" × 1.5" footprint for line driver
• low profile – has 1.5" maximum height (driver 0.75-high)
• low power dissipation – draws less than 200 W DC draw
• lightweight – weighs less than 2.5 lb
• low cost – uses minimum number of MMICs to generate 25 W output
With these features, the new DPA enables integrators to offer the smallest, lightest and lowest cost high performance mobile satcom terminals available.
Wavestream,
San Dimas, CA (909) 599-9080,
www.wavestreamcorp.com.
